Two layers can result when two micelle spheres combine and flatten out. The hydrophobic tails end up located away from water, the heads are on the outside, and two layers line up back to back.
Tails at the ends of sheets are protected if the sheets are curled into sacs. This makes a lipid bilayer membrane, one ressembling the outside of an animal cell, or a vessicle.
Many cell components, such as hemoglobin, are surrounded by a lipid membrane.
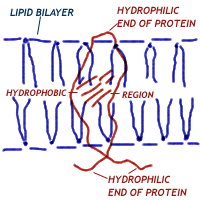
The membrane acts as a flexible foundation in which proteins do their work. For example, there are channels through neuron membranes through which ions flow.
Now we understand how water can influence a molecule through its charges, let's ENTER THE WORLD OF PROTEINS!
Home-+-Index-+-